The Logical Operations creation modality allows you to create new events by applying logical operations to existing ones.
The left panel appears as follows:
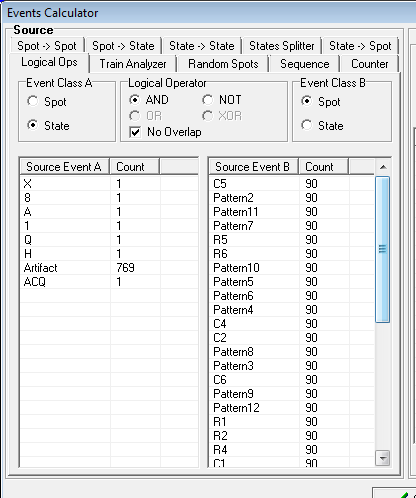
Depending on the events classes (Spot or State) and logical operator, there are 5 different main situations, that will be illustrated in the next table. Note that black and red lines indicates the two operands, while the blue lines indicate the results of the logical operation. Horizontal lines indicates time, while vertical lines indicate spots and rectangles indicate states. Operations are performed on a sample by sample basis.
Operands |
Operators |
Example |
Spot vs. Spot generates a Spot |
There are three defined boolean operations:
|
|
Spot vs. State generates a Spot |
There is only one defined boolean operation: AND |
|
Unary Operator on a State generates a State |
The only defined unary operation on a State is the NOT |
|
State vs. Spot generates a State |
The only defined boolean operation is the AND |
|
State vs. State generates a State |
There are three defined boolean operations:
|
|
Created with the Personal Edition of HelpNDoc: Create HTML Help, DOC, PDF and print manuals from 1 single source