Typical ERP measures are available from the ERP module, and can be set from the ERP macro (Average Builder) form. An unlimited number of ERP measures can be associated to each macro, so that every time a new average is computed, the measures are also automatically computed. Measures are relative to sensors and can be associated to one or two time points.
There are 4 different possible configurations (1 or 2 sensors, and 1 or 2 time point) and six possible measures, which can be enabled or not depending on the number of sensors and time points.
The form relative to the each measure creation appears as the following one:

In the central part the user has to select the number of sensors and time points to use. Sensors can be selected from the two lists, one on both sides of the form. Similarly, from two groupboxes on both sides (Time 1 and Time 2) it is possible to select the exact time to be used: in particular, the Latency parameter indicates the time relative to the trigger instant. As peaks might vary among subjects (e.g. P300 peak indicates that "around" 300ms after target stimuli a Positive deflection is usually observable), it is possible to let NPXLab to find the peak according to 5 different functions ("Local Peak" subgroup):
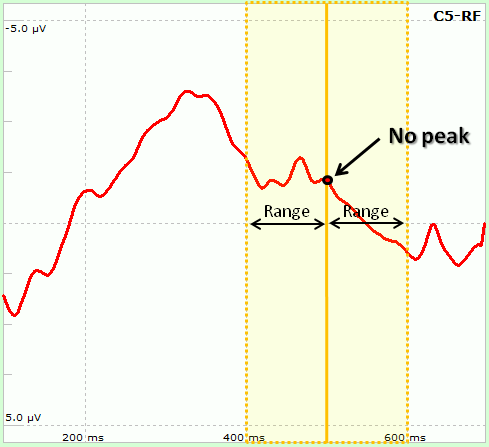
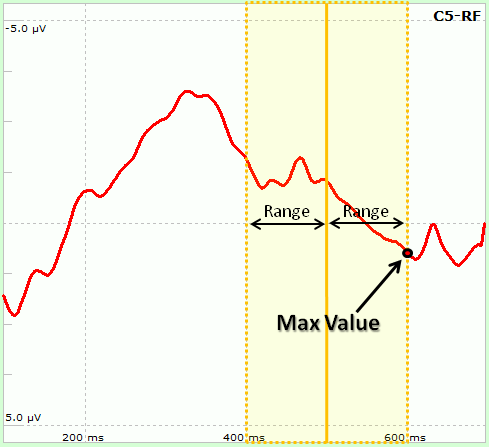
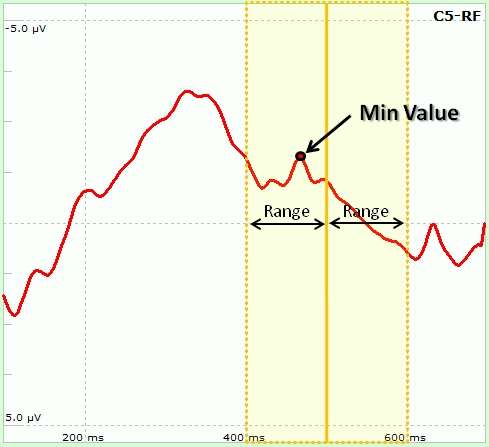
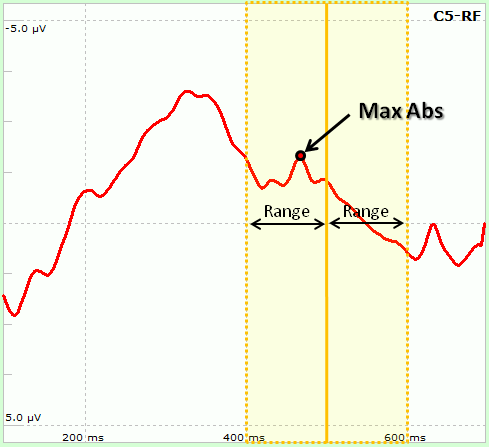
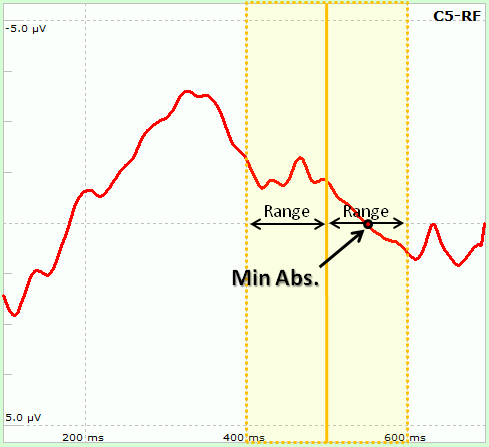
Some of the settings can be enabled/disabled depending on the measure type. The nine different possible measures are:
Sensors |
Time Points |
Measure |
|
|
1 |
1 |
Amplitude: the amplitude of the selected sensor at time T1 |
|
1 |
1 |
Latency: the T1 latency value, identified by its amplitude |
|
1 |
2 |
Amplitude Difference: the amplitude of the selected sensor at time T1 minus the amplitude of the same sensor at time T2 |
|
1 |
2 |
Latency Difference: the difference T2 - T1, identified by the sensor |
|
1 |
2 |
Area: the area of the signal of the selected sensor in the interval [T1; T2] |
|
1 |
2 |
Mean: the area of the signal of the selected sensor in the interval [T1; T2]. It is computed as Area / abs(T2 - T1) |
|
2 |
1 |
Amplitude Difference: the difference of the amplitudes of two sensors at time T1 |
|
2 |
2 |
Amplitude Difference: the difference of amplitude relative to the first sensor at time T1 and that of the second sensor at time T2 |
|
2 |
2 |
Latency Difference: the difference between T2 computed on the second sensor and T1 computed on the first sensor |
Created with the Personal Edition of HelpNDoc: Create HTML Help, DOC, PDF and print manuals from 1 single source